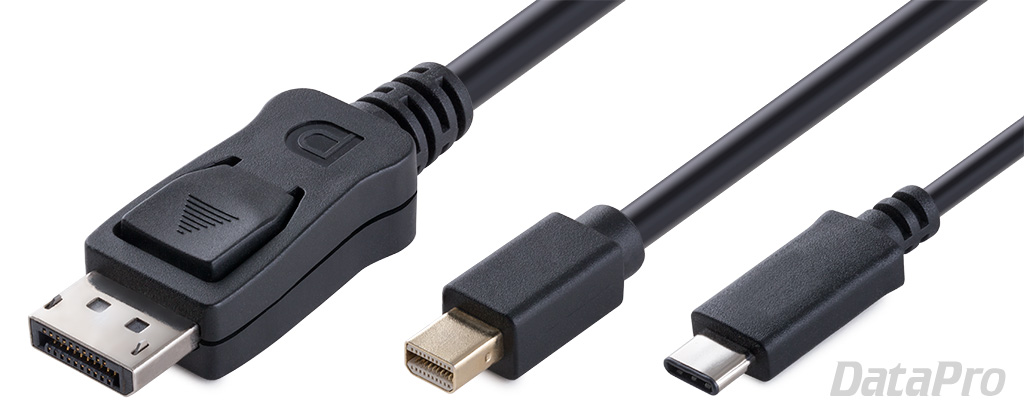
DisplayPort is a digital display and data transfer interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), a coalition of technology companies that includes Apple, AMD, Samsung, HP, Lenovo, and others.
DisplayPort is a digital display and data transfer interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), a coalition of technology companies that includes Apple, AMD, Samsung, HP, Lenovo, and others.
Introduced in 2006 as a successor to DVI, it is often seen as a video connection on higher-end desktop computers. Its compact version (Mini DisplayPort) is also widely known as the physical format used by Thunderbolt versions 1 and 2. This guide will answer common questions about its functionality, use, and performance.
Index:
Basic info:- What is DisplayPort?
- What is the difference between DisplayPort 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 2.0?
- What is Mini DisplayPort?
- What's different about DisplayPort 2.0?
- What is the relationship between DisplayPort and USB4?
- DisplayPort vs VGA and DVI
- DisplayPort vs Thunderbolt
- DisplayPort vs HDMI
- What is the maximum length of a DisplayPort cable?
- How do I extend DisplayPort?
- How do I get sound through DisplayPort?
- How do I tell my version of DisplayPort?
- How do I use a single DisplayPort port for multiple monitors?
- Can I daisy-chain multiple monitors from a single DisplayPort port?
- What is the difference between Active and Passive DisplayPort adapters?
- What is Dual-Mode/Multimode DisplayPort?
- What is DisplayPort Alternate Mode?
- What is DisplayPort Deep Sleep?
- What is Embedded DisplayPort?
- Did Dell develop DisplayPort?
- What kind of Panel-Mount DisplayPort options are available?
Learn more about digital video!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on digital video, data cabling,
networking, and more!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on digital video, data cabling,
networking, and more!
What is DisplayPort?
DisplayPort is a digital display and data transfer interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) in 2006. Like its contemporary competitors, HDMI and Thunderbolt, it is a composite format capable of carrying video, audio, and data simultaneously. It can typically be found on desktop PCs, where it's not quite as common as HDMI, but more popular than ThunderboltWhat is the difference between DisplayPort 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 2.0?
Since 2006, VESA has consistently released new versions of DisplayPort every few years. These tend to improve on the following areas:- Resolution
- Bandwidth
- Sound support
- Feature support
| Published | Max Bandwidth | Max Resolution | Notable Features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DisplayPort 1.0 | 2006 | 10.80 Gbps | 4K @ 30 Hz | Original version |
| DisplayPort 1.1 | 2007 | 10.80 Gbps | 4K @ 30 Hz | HDCP, Link Layers |
| DisplayPort 1.2 | 2010 | 21.60 Gbps | 5K @ 30 Hz | 3D, HBR2 |
| DisplayPort 1.3 | 2014 | 32.40 Gbps | 8K @ 30 Hz | HDMI 2.0, HDCP 2.2 |
| DisplayPort 1.4 | 2016 | 32.40 Gbps | 8K @ 60 Hz | DSC, HBR3 |
| DisplayPort 2.0 | 2019 | 80.00 Gbps | 16K @ 60 Hz | Improved multi-display and VR/AR support |
What is Mini DisplayPort?
Mini DisplayPort is a compact version of the DisplayPort connector introduced by Apple in 2008. Mini DisplayPort is free to license, and in 2009 it was included in the official DisplayPort 1.2 spec. In 2011, Apple and Intel announced the Thunderbolt format, which used the same physical connector, but significantly different protocols. Mini DisplayPort can be adapted to and from DisplayPort with a passive adapter.Related products:
What's different about DisplayPort 2.0?
DisplayPort 2.0 uses a more efficient encoding scheme for a maximum throughput of 80 Gbps. This allows it to support displays up to 16K, or more practically, multiple 4K or 8K displays. This is also useful for VR, which can involve multiple high-resolution displays running at high framerates.What's the relationship between DisplayPort and USB4?
With the introduction of USB-C, DisplayPort could be used as an "alt mode", allowing it to output directly from a USB-C port. In USB4, DisplayPort is even more tightly integrated as part of the USB4 standard. This means DisplayPort can be routed over USB4 topography, such as through hubs or other devices, provided they comply with the USB4 spec.DisplayPort vs VGA and DVI
VGA and DVI are legacy formats that preceded DisplayPort. In almost all respects, DisplayPort outclasses both DVI and VGA in terms of bandwidth, versatility, and ease of use. Perhaps the only exception is VGA's impressively long range (as much as 150-200ft), though that comes at the cost of maximum resolution. DisplayPort can easily support a DVI or VGA display via passive adapters.Related products:
DisplayPort vs Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt is a computer interface co-developed by Intel and Apple. It combined both DisplayPort and PCI Express into one physical connection - the Mini DisplayPort connector. As of Thunderbolt 3, its physical form factor has been updated to use USB Type-C.A Thunderbolt port will generally support most DisplayPort features, and can be adapted to DisplayPort with a passive adapter, the reverse is not true.
Related products:
DisplayPort vs HDMI
Depending on the version, DisplayPort and HDMI tend to be roughly equal in performance and capability, with HDMI edging out DisplayPort as the more popular format, and DisplayPort winning in overall bandwidth. A DisplayPort jack can be adapted for use with an HDMI display using this adapter, but connecting a DisplayPort display to an HDMI source can be more difficult. For more information, check out our HDMI Info page here.Related products:
What is the maximum length of a DisplayPort cable?
The DisplayPort spec calls for full bandwidth transmission at lengths up to 6.5ft (2M), and reduced functionality (1920x1080p at 60 Hz) up to 50ft (15M).Related products:
How do I extend DisplayPort?
DisplayPort can be extended with a passive cable up to its maximum spec length. Keep in mind however that multiple connections can weaken the signal, so daisy-chaining extensions may result in a shorter practical maximum length.Related products:
How do I get sound through DisplayPort?
Multi-channel audio support is part of the DisplayPort spec, but its availability depends upon manufacturer implementation.DisplayPort audio depends on three things:
- An output device (PC, laptop, or video card) that supports DisplayPort audio or dual-mode with audio.
- A display capable of playing audio - such as a monitor with speakers or a television.
- A dual-mode adapter if the display has an HDMI input.
How do I tell my version of DisplayPort?
Unfortunately there's no way to tell from the hardware itself what version of DisplayPort it will support. Check the original specifications of your device, or contact the manufacturer.How do I use a single DisplayPort port for multiple monitors?
You can either daisy-chain them (see below) or use USB4 hubs to route the DisplayPort signal as needed.Can I daisy-chain multiple monitors from a single DisplayPort port?
Starting with DisplayPort 1.2, the "multi-stream" feature allows what's more commonly known as daisy chaining, or the ability to chain multiple monitors together while connected to a single DisplayPort port.Using this feature requires two things:
- A source device, such as a computer that supports at least DisplayPort 1.2.
- DisplayPort-compatible monitors with both 'In' and 'Out' DisplayPort jacks.
What is the difference between Active and Passive DisplayPort adapters?
Passive adapters convert only the physical format of the connector, while Active adapters actually transcode the signal and change the physical format.DisplayPort can be passively converted to Single-Link DVI and HDMI. VGA, Dual-Link DVI, and other formats require an Active adapter.
For more information see: What is Dual-Mode DisplayPort?
Related products:
What is Dual-Mode/Multimode DisplayPort?
Dual-mode is DisplayPort's ability to output either DisplayPort, HDMI, or Single-Link DVI from the same port. The advantage to this is that Passive adapters can be used to make the conversion -- these are typically smaller and cheaper than the Active variety, and don't require external power.However Passive adapters are limited to resolutions that the DisplayPort device's Multi-Mode implementation supports -- rather than the maximum resolution the device is capable of outputting via DisplayPort.
For example, DisplayPort only supported a passive HDMI resolution of 1080p for many years, but it was still possible to coax 4K HDMI out of it with an Active adapter. And an Active adapter has always been required to adapt DisplayPort to Dual-Link DVI.
What is DisplayPort Alternate Mode?
Alternate Mode is a feature of USB Type-C that allows a USB-C that's similar to Dual-mode DisplayPort. It allows the physical USB-C port to support other video and data formats - one of which is DisplayPort. Note that Dual-Mode is not available from an Alt Mode connection.Related products:
What is DisplayPort Deep Sleep?
Deep Sleep is an energy saving option on some DisplayPort monitors that puts them in an especially low power mode rather than cutting power entirely. This allows the monitor to 'wake' more quickly than from a cold start, while conserving more energy than typical Sleep mode. In combination with some source devices and video cards, people have reported that disabling this feature solves issues with a computer or monitor being unable to awake from Sleep.What is Embedded DisplayPort?
eDP, or Embedded DisplayPort was introduced in 2008 with the aim of standardizing the connection between laptop graphics cards and built-in display panels. Its latest version is 1.4, released in mid-2016.Did Dell develop DisplayPort?
Dell is a member of the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA) working group that developed the DisplayPort standard, and was the first company to release DisplayPort hardware. Other prominent members of the work group included HP and Lenovo.What kind of Panel-Mount DisplayPort options are available?
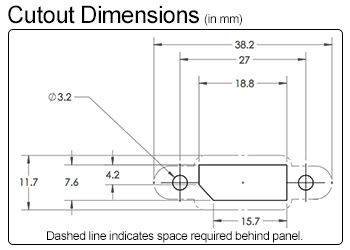
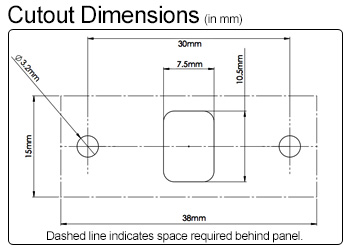
DataPro carries a variety of panel-mount DisplayPort cables, including a Panel-Mount Extension and Panel-Mount Coupler, which use the same cutout, as shown below:We also carry a Panel-Mount Mini DisplayPort Extension and Panel-Mount Mini DisplayPort to DisplayPort Extension, which use the cutout below:
Related products:
Learn more about digital video!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on digital video, data cabling,
networking, and more!
Check out our other tech articles for more information on digital video, data cabling,
networking, and more!